


 LUDWIG PICK
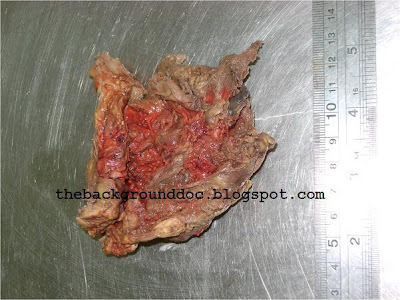
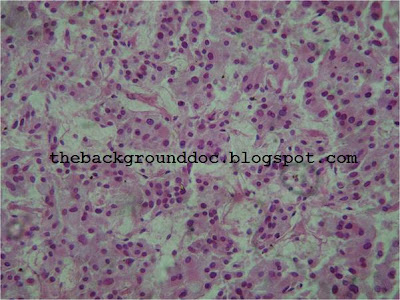
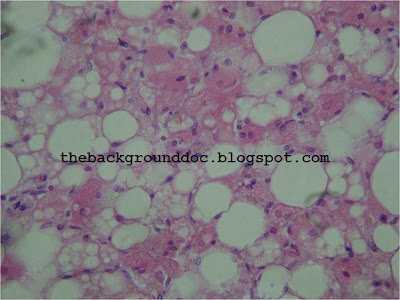
LUDWIG PICK"The first description of the adrenal gland dates since 1563 by Eustachius in a study "Opuscula anatomica". Despite earlier recognition of the presence of adrenals and division into cortex and medulla, the precise observations of Addison appeared in 1855 that the essential role of these glands was recognized in patients who died with adrenal destruction secondary to tuberculosis. Frankel first described a medulary adrenal tumour in 1886. In 1912 the pathologist Pick formulated the descriptive term pheochromocytoma. The first surgical removal of pheochromocytoma in Europe was performed by Rouks in 1926 and by Mayo in USA in 1927."
Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2002 Jul;130 Suppl 2:31-7.

Professor Ludwig Pick (August 31, 1868 - February 3, 1944) was a German pathologist who was a native of Landsberg an der Warthe. In 1893 he earned his medical doctorate in Leipzig, and subsequently practiced medicine at Leopold Landau's private Frauenklinik, where he remained until 1906. That same year he became director of the department of pathological anatomy at the city hospital Friedrichshain-Berlin. Later, he was imprisoned by the Nazis, and died on February 3, 1944 at the Theresienstadt Concentration Camp.
Ludwig Pick made several contributions to academic pathology, particularly in the field of genitourinary diseases, and also in the study of melanotic pigmentation. In 1912 he coined the term pheochromocytoma to describe the chromaffin color change in tumor cells associated with adrenal medullary tumors.
No comments:
Post a Comment